Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Physical Engineering, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, China
2 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Laser Polarization and Information Technology, Research Institute of Laser, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, China
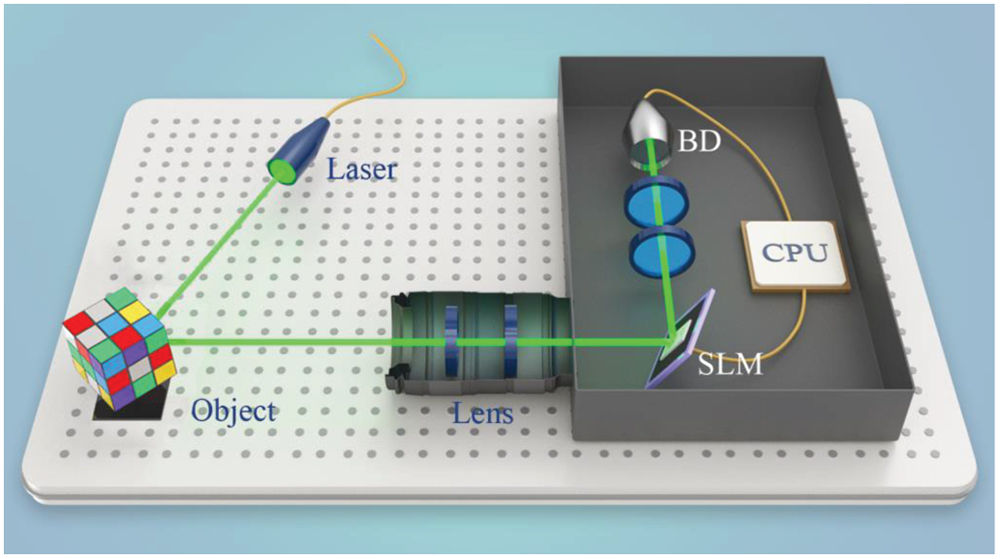
Computational ghost imaging (CGI) has recently been intensively studied as an indirect imaging technique. However, the image quality of CGI cannot meet the requirements of practical applications. Here, we propose a novel CGI scheme to significantly improve the imaging quality. In our scenario, the conventional CGI data processing algorithm is optimized to a new compressed sensing (CS) algorithm based on a convolutional neural network (CNN). CS is used to process the data collected by a conventional CGI device. Then, the processed data are trained by a CNN to reconstruct the image. The experimental results show that our scheme can produce higher quality images with the same sampling than conventional CGI. Moreover, detailed comparisons between the images reconstructed using the deep learning approach and with conventional CS show that our method outperforms the conventional approach and achieves a ghost image with higher image quality.
computational ghost imaging compressed sensing convolutional neural network Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(10): 101101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
In this letter, we analyze the effects of light intensity on reflective ghost imaging with thermal source. We find that the brightness of reflective ghost image can be changed by modulating the light intensity of the source and the splitting ratio of the beam splitter. The signal-to-noise ratio will be improved by increasing the light intensity of the source. More important, we can obtain the reflective ghost image with high image quality by adopting a low light intensity signal beam and a high light intensity reference beam, which is better than the classical optical imaging, because it can reduce the effects of light on the object.
270.5290 Photon statistics 030.6600 Statistical optics Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(7): 072701
1 曲阜师范大学物理工程学院山东省激光偏光与信息技术重点实验室, 山东 曲阜 273165
2 济宁学院物理与信息工程系, 山东 曲阜 273155
利用弱测量技术研究两量子比特的量子关联动力学演化和转移。有纠缠突然死亡现象产生的非最大纠缠初态经前选择测量操作后,在演化过程中不但能够提高量子关联强度,而且能够缩短甚至消除量子比特纠缠的突然死亡区域;而对于演化中无纠缠突然死亡的非最大纠缠初态,弱测量操作则会降低量子比特间关联强度。对初始处于最大纠缠态的粒子,弱测量操作不能增强粒子间的纠缠但可以优化量子关联中的量子失谐。弱测量在实现量子关联转移时的破坏极小,能够延迟纠缠的衰减,并可使量子纠缠的转移时间提前。另外腔场与量子比特间的耦合强度与系统耗散率的关系决定纠缠原子在腔中动力学演化,表现为马尔可夫和非马尔可夫过程。
量子光学 弱测量 共生纠缠 量子失谐 纠缠突然死亡 量子关联转移 光学学报
2013, 33(11): 1127001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
In this letter, we use quantum description and the Gaussian state to study reflective ghost imaging with two classical sources, and to provide their expressions. We find that the reflective ghost imaging of a rough-surfaced object, using Gaussian-state phase-insensitive or classically correlated phase-sensitive light, can be expressed in terms of the phase-insensitive or phase-sensitive cross-correlations between the two detected fields, including a background term. Moreover, reflective ghost imaging with two classical Gaussian-state lights is shown to have similar features as spatial resolution and field of view.
110.0110 Imaging systems 270.0270 Quantum optics 030.0030 Coherence and statistical optics Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(3): 031102





